This week’s science news featured a surge of remarkable astronomical observations, highlighted by groundbreaking discoveries concerning the origins of comet 3I/ATLAS.
An interstellar comet, first observed in late June, is now yielding significant insights into its ancient origins and age. Scientists suggest this celestial visitor likely emerged from the far reaches of our galaxy and could even be a pristine relic from its earliest formation. This lineage would potentially make the comet billions of years older than the sun itself.
Further observations have highlighted the comet’s distinctive behavior, with astronomers reporting it spewing water “like a fire hose” at an unprecedented distance from the sun. Researchers continue to maintain a close watch on the object, even deploying the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Mars spacecraft to capture the most detailed images yet of its bright coma.
Significant astronomical discoveries unfolded far from Earth, with a radio telescope achieving the unprecedented feat of imaging two black holes orbiting each other. Scientists also reported tentative findings suggesting the existence of controversial dark matter stars. Moreover, the James Webb Space Telescope delivered a powerful affirmation of Albert Einstein’s theories, identifying eight remarkable gravitational lenses that beautifully illustrate the warping of spacetime.
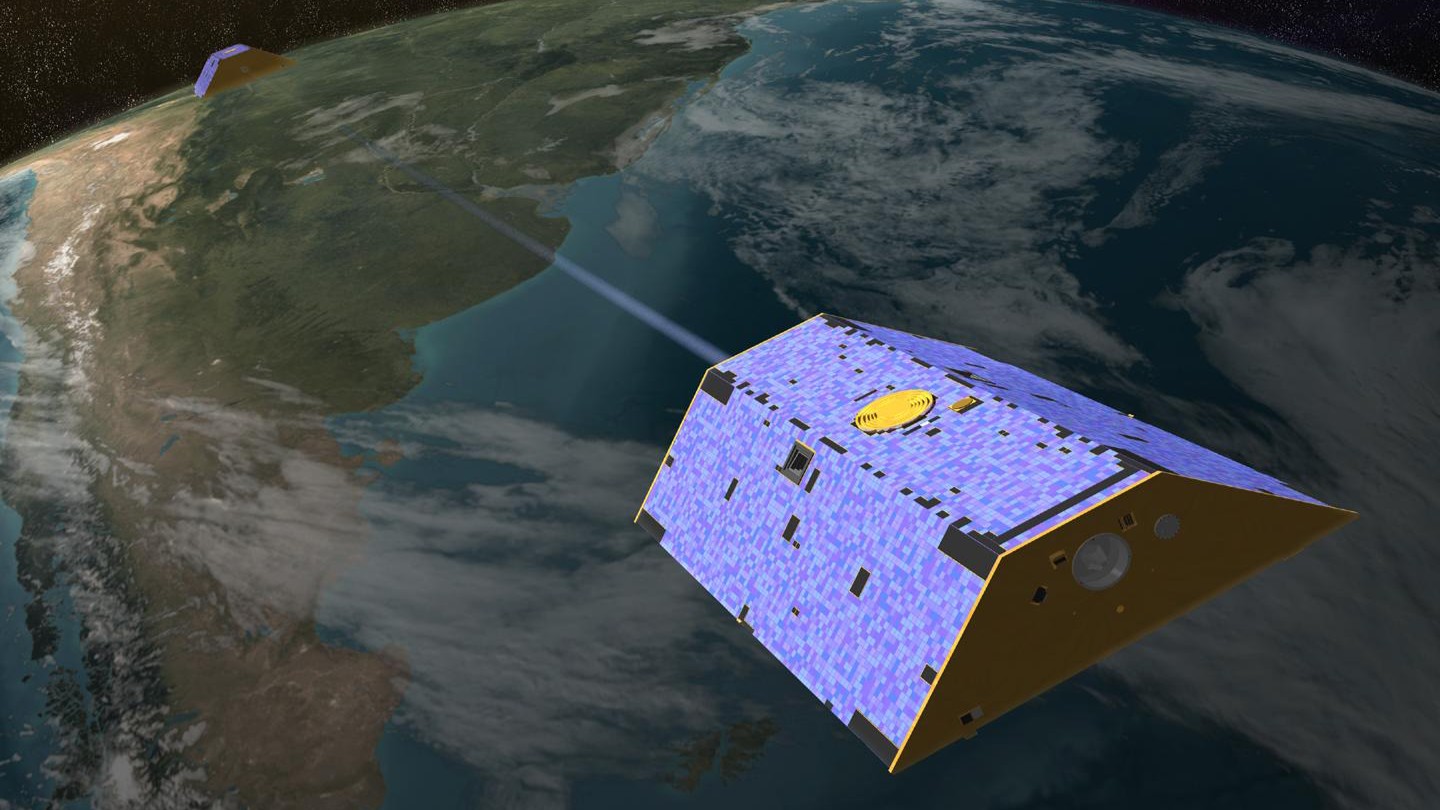
In 2007, a colossal gravity anomaly, spanning the length of the African continent, emerged simultaneously with a notable geomagnetic ‘jerk’ observed in Earth’s gravitational field.
A curious gravitational anomaly, marked by both a distinct signal and a sudden “jerk,” endured for approximately two years. Yet, its presence remained undetected for 18 years, only to be finally revealed within the extensive data collected by satellites charting Earth’s gravitational field.
Scientists are now proposing that a newly identified geological process, believed to originate near Earth’s core through a rapid redistribution of mass in its deep mantle, accounts for the phenomenon in question. Nonetheless, extensive additional research is imperative to fully grasp these hidden processes and their broader repercussions.
Uncover the pivotal news and ongoing transformations affecting Planet Earth.
The Coral Triangle, a vast and biodiverse marine expanse often likened to the “Amazon beneath the sea,” is reportedly exhibiting a notable degree of resilience to the escalating impacts of climate change.
Scientists have announced an intriguing discovery: the presence of gold nanoparticles nestled within the needles of spruce trees.
Six million years ago, the Red Sea was gripped by an environmental upheaval so profound it ranks as one of Earth’s most extreme natural events.
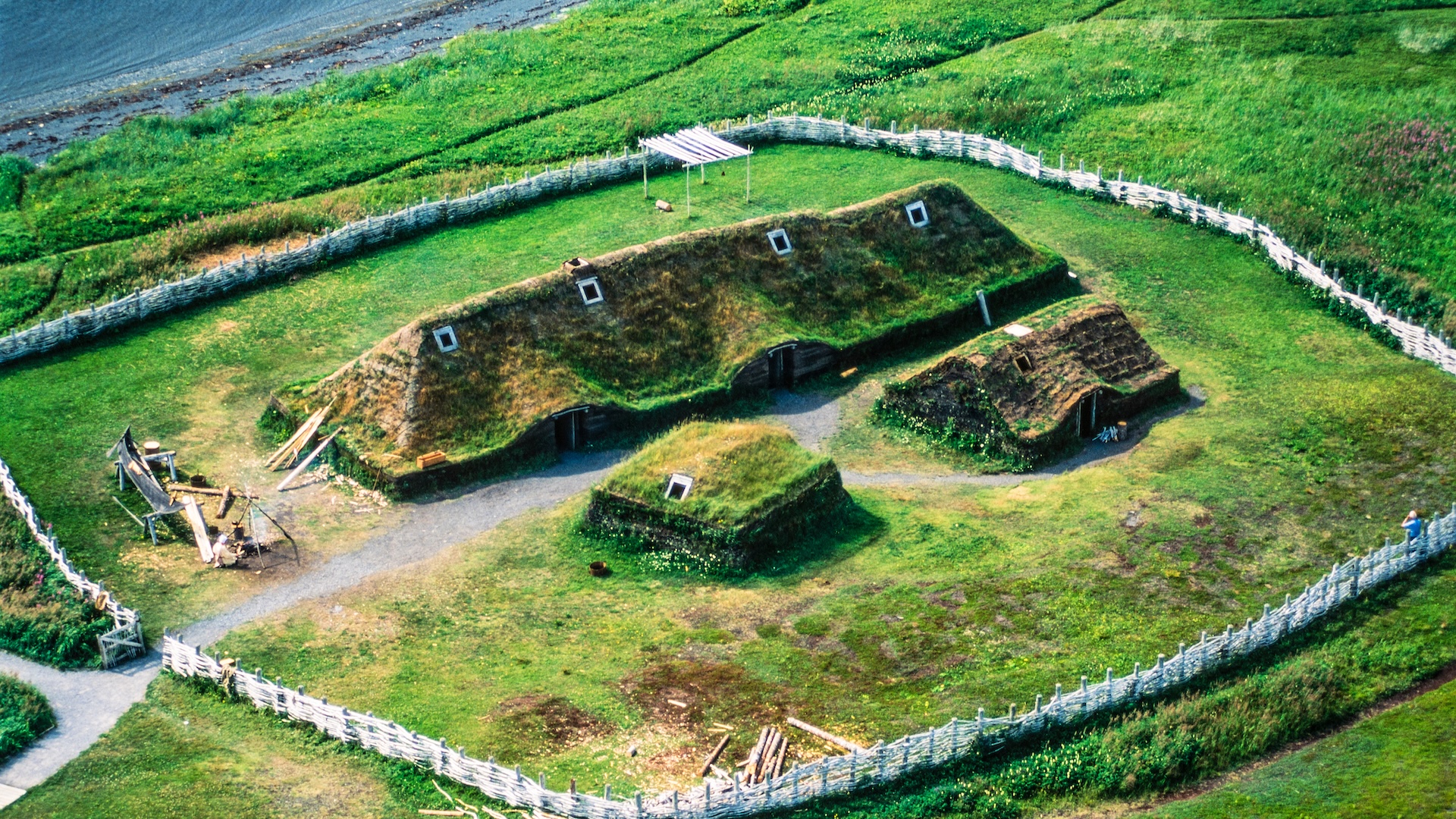

Despite widespread narratives, Christopher Columbus was not the initial European to encounter the Americas. His celebrated arrival in the Western Hemisphere actually placed him among the very last of those historically attributed with its discovery, long after numerous others had already made contact.
The recent investigation into a significant historical discovery has unearthed a vast 23,000-year narrative spanning humanity’s prehistoric past. This journey through ancient history spotlights the early presence of diverse groups, including Native Americans, Viking explorers, and Polynesian seafarers, who navigated and settled long before European arrival on the continent.
—If you enjoyed this, sign up for our Life’s Little Mysteries newsletter

Scientists have developed an artificial intelligence capable of generating entirely novel viruses. These newly created viruses are bacteriophages, specifically engineered to target and infect bacteria, not human cells. Researchers confirm that stringent protocols were followed to ensure the AI’s models could not design pathogens harmful to people, animals, or plants.
While the creators of a new scientific discovery herald its potential to eradicate antibiotic-resistant superbugs, a darker prospect looms. Other research indicates that vulnerabilities and workarounds could allow artificial intelligence models, or malevolent human actors utilizing them, to engineer potentially catastrophic diseases. This raises concerns that what appears to be a medical breakthrough might also harbor the seeds of a disastrous, even apocalyptic, future.
Though current limitations avert an immediate danger, humanity’s fragmented approach to AI regulation risks accelerating its emergence, potentially making it a reality sooner than expected.
For additional health updates and analysis.
Chemotherapy, while vital in fighting cancer, poses a significant challenge by damaging healthy cells in addition to malignant ones. However, scientists are exploring nanoparticles as a potential innovation to overcome this indiscriminate effect, aiming for more targeted treatment.
A perplexing medical mystery centered on a woman who endured a lifetime of involuntary, mirthless laughter, a condition ultimately traced to an unusual brain lesion. The case presented a significant diagnostic challenge for clinicians.
The potent venom of the mamba snake typically leads to muscle paralysis. Yet, a paradox emerges: the very antivenom meant to restore function can occasionally drive muscles into an overactive state.
Robots are set to receive a significant boost in intelligence, an advancement spearheaded by Google DeepMind’s new ‘thinking AI’. This innovative system, which comprises a pair of sophisticated models, is designed to profoundly enhance machines’ capacity to understand their environment.
Three researchers have been jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their pioneering work on advanced materials, drawing intriguing parallels to the magical creations depicted in the ‘Harry Potter’ saga.
The recent identification of a Jurassic-era species, colloquially known as the ‘sword dragon,’ is anticipated to provide crucial insights into a long-standing evolutionary enigma.
New analysis indicates that Sir Ernest Shackleton’s legendary polar ship, the Endurance, was beset by multiple structural deficiencies.

Climate change is ushering in an intensifying era of natural disasters, marked by devastating wildfires, powerful tornadoes, severe heatwaves, and widespread floods. These extreme weather events are exacting a substantial economic toll, with damages projected to exceed $100 billion by June 2025 alone. Scientists widely anticipate this concerning trend to worsen over time.
A curated collection of this week’s most compelling book excerpts, thought-provoking opinions, and challenging science crosswords is now available, offering substantive material for weekend reading.
Epidemiologist Michael Osterholm contends that a future pandemic, ominously labeled “The Big One,” has the potential to be more severe than COVID-19, emphasizing the vital lessons to be gleaned from historical outbreaks.
A recent commentary asserts that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is experiencing significant weakening under the Trump administration, reportedly leading to immediate and noticeable public health consequences.
China has unveiled an updated commitment to curb its greenhouse gas emissions. This new pledge immediately raises a significant question: does this move position the nation as a leading force in global climate action?
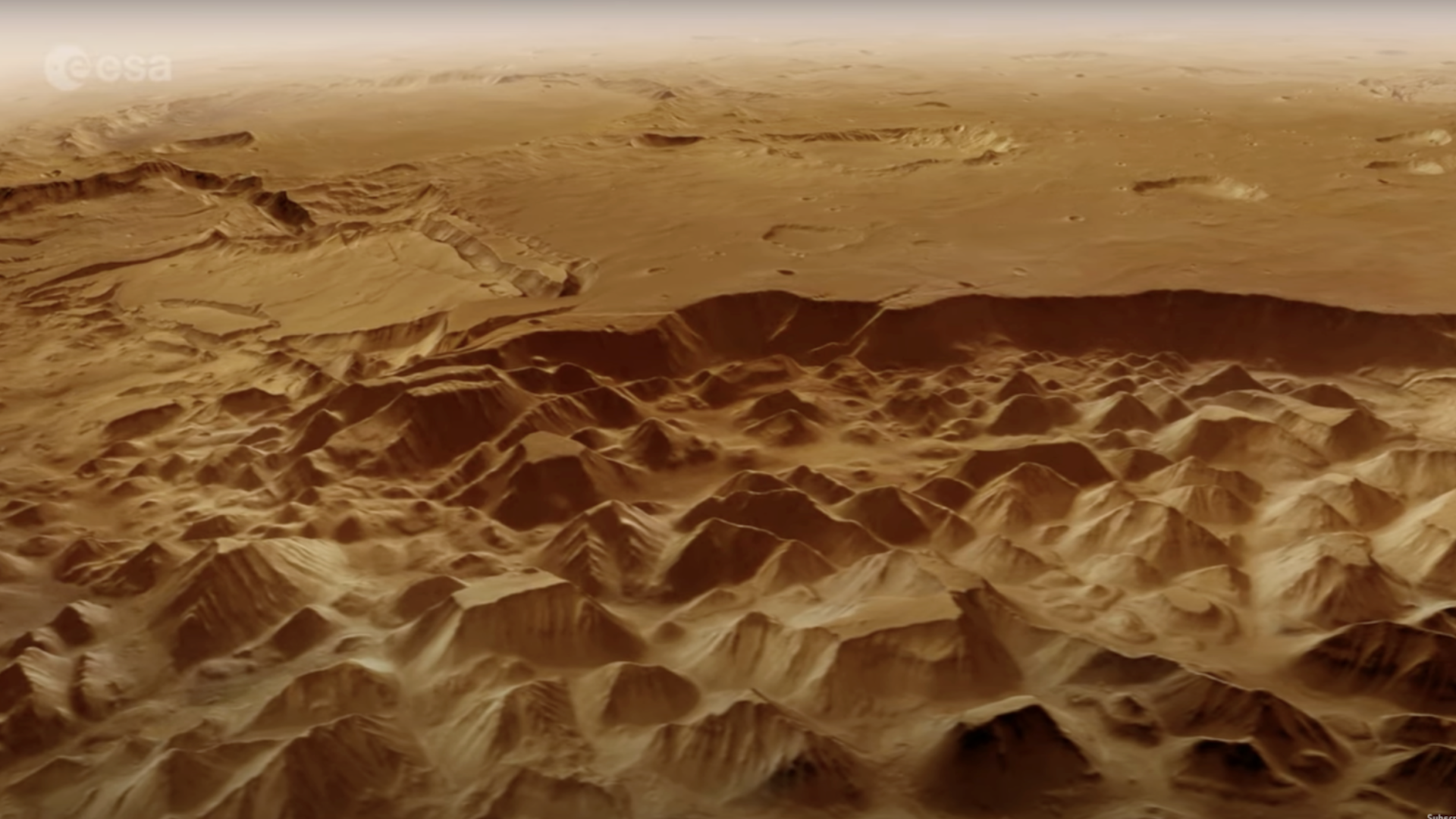
The European Space Agency (ESA) has released a new animation, inviting viewers on an immersive virtual flight across the Martian surface. Crafted from detailed data acquired by the Mars Express spacecraft, the video delivers a breathtaking aerial perspective of the Red Planet. This stunning journey showcases ancient riverbeds, glides over weathered islands, and culminates with a dramatic vista of a colossal asteroid impact crater.
Want more science news? Follow our Live Science WhatsApp Channel for the latest discoveries as they happen. It’s the best way to get our expert reporting on the go, but if you don’t use WhatsApp we’re also on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), Flipboard, Instagram, TikTok, Bluesky and LinkedIn.







